-

Diploma in Guidance and Counselling
The increasing awareness around mental health and the need for professional support has created a growing demand for trained counselors. A Diploma in Guidance and Counselling offers an ideal pathway for individuals interested in helping others navigate their personal and emotional challenges. Whether you’re looking to work in schools, hospitals, or private practice, this diploma…
-

Hamad Al Wazzan’s Perspective on Managing Debt
Debt can be a double-edged sword. On one side, it enables people to access opportunities they might not otherwise afford, like buying a home or starting a business. On the other, it can become a crushing burden when mismanaged. Hamad Al Wazzan, a respected figure in finance and investment, has often emphasized that debt, when…
-

Tax Saving Fixed Deposits (FDs) in India: A Complete Guide
Tax-saving fixed deposits (FDs) are one of the most popular and safest investment options for individuals looking to save taxes while earning stable returns. Under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act, investments in tax-saving FDs are eligible for deductions, providing a dual benefit of tax savings and guaranteed returns. In this guide, we’ll explore…
-

Rajkot Updates News When Will the Tesla Phone be Released
Tesla Phone Overview (Rumoured) The Tesla Pi Phone has been a hot topic among tech enthusiasts and Tesla fans alike. While still a rumor, this innovative device is expected to revolutionize the smartphone industry with cutting-edge features and a focus on sustainability. Tesla, under Elon Musk’s visionary leadership, has disrupted multiple industries, and the smartphone…
-
كيف يواجه صخر التون تحديات السوق؟
في مشهد تنافسي وغير متوقع أحيانًا مثل سوق السيارات في العراق، برز صخر التون كرائد ومبتكر. بصفته قائد شركة ALT SAK FZE، نجح التون في تجاوز العديد من التحديات، بدءًا من التقلبات الاقتصادية وصولاً إلى تغيّر احتياجات المستهلكين. بفضل استراتيجياته المستقبلية وتركيزه الدائم على الابتكار، تمكن من تأمين موقع الشركة كرائدة في السوق ووضع معايير…
-

Kristen Archives: Guide to This Controversial Erotic Fiction Library
Intropduction: The Kristen Archives is an online platform that serves as a repository for a wide variety of erotic stories, primarily aimed at consenting adults. It features user-submitted narratives that explore diverse themes and sexual experiences, often categorized by genre and content type. While the site is intended for adult audiences, it has faced criticism…
-
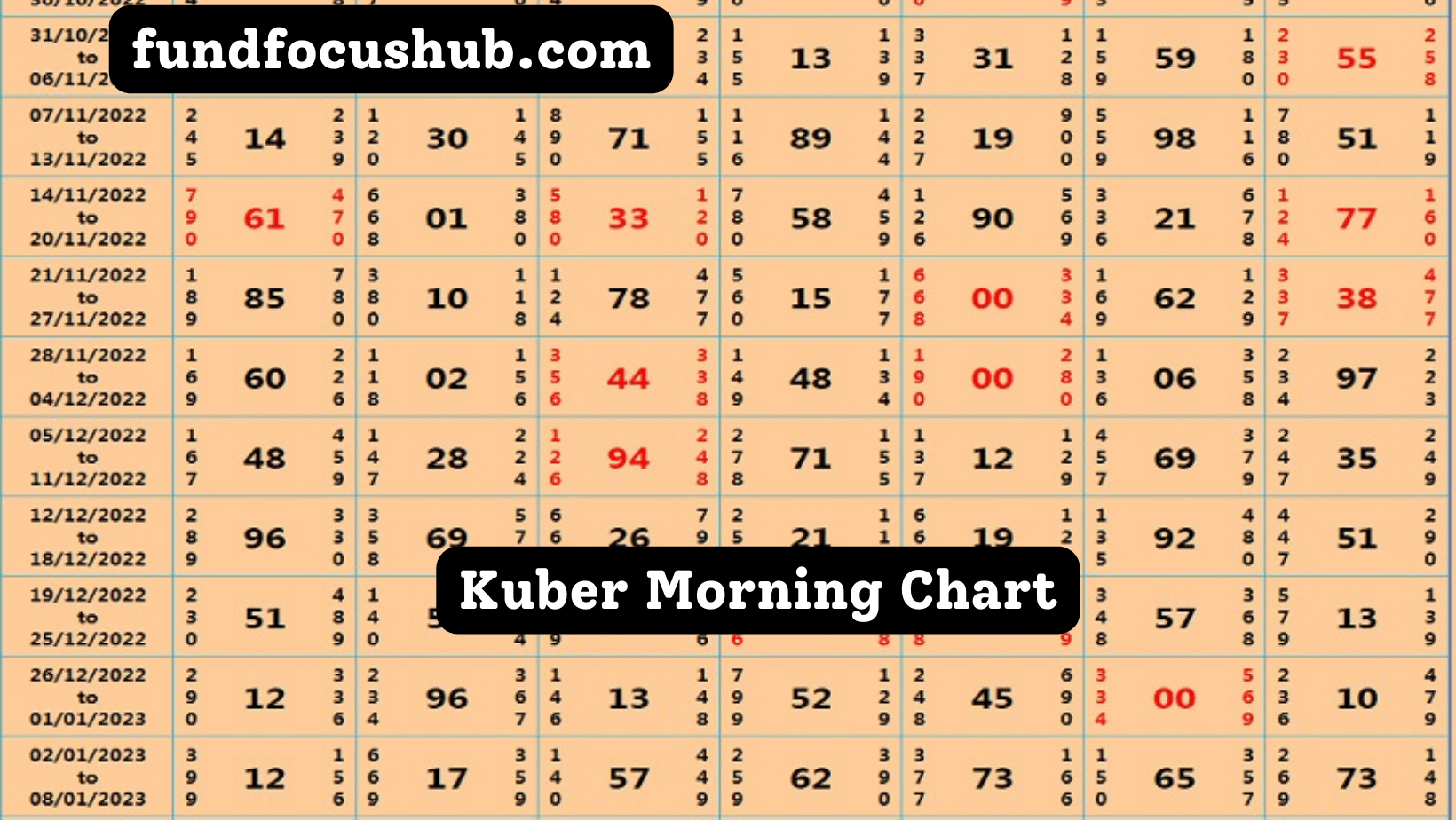
Kuber Morning Chart: Daily Draw Insights
Introduction The world of Satta Matka betting is steeped in strategy, trends, and statistical analysis. At the heart of this lies the Kuber Morning Chart, a fundamental tool used by players to predict outcomes, analyze patterns, and make strategic bets. For both new players and seasoned veterans, understanding this chart is crucial for making informed…
Follow Me On Instagram
@WillamSmith